_1735534305_1736409856.png)
Ensuring Development of Quality Seeds And Reaching to The Farmer's Doorstep.
Our Certification
_1733140295.png)


Our Achievements
_1733131691.jpg)
_1733131691.jpg)
_1733131691.jpg)

Home
CROPS
Pumpkin
Bitter Gourd
Bottle Gourd
Egg Plant
Uchche
Tomato
Red Amarnath
Ridge Gourd
Snake Gourd
Sponge Gourd
Wax Gourd
Cucumber
Khira
Watermelon
Melon
Squash
Chili
Capsicum
Cabbage
Cauliflower
Broccoli
Kholrabi
Raddish
Carrot
Red Beet
Okra
Onion
Papaya
Bean
Country Bean
French Bean
Lettuce
Coriander
Stem Amaranth
Green Leaf Amaranth
Spinach
Kalmi spinach
Indian Spinach
Marigold
Cotton
Jute
Mustard
Soybean
Mung beans
Lentils
Wheat
Corn
Potato
.png)
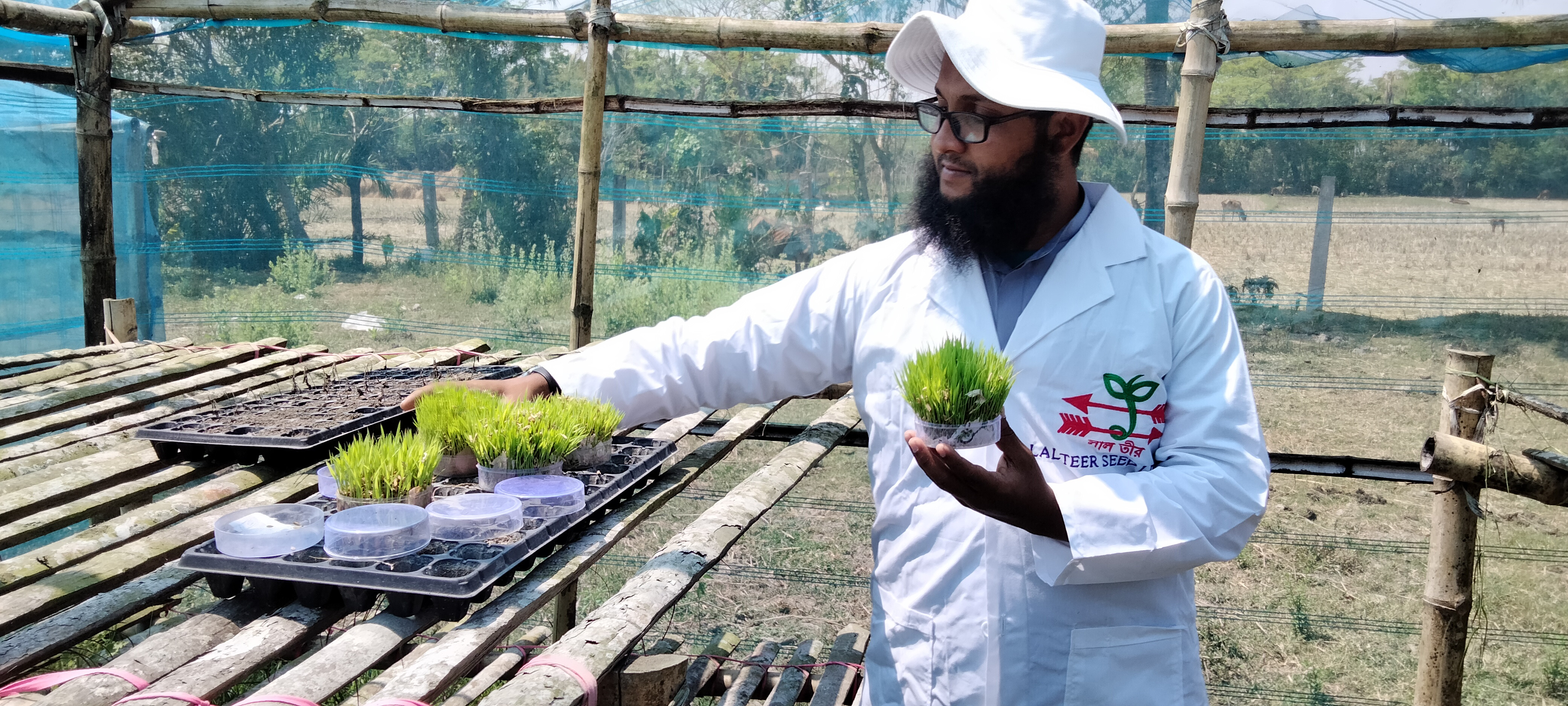
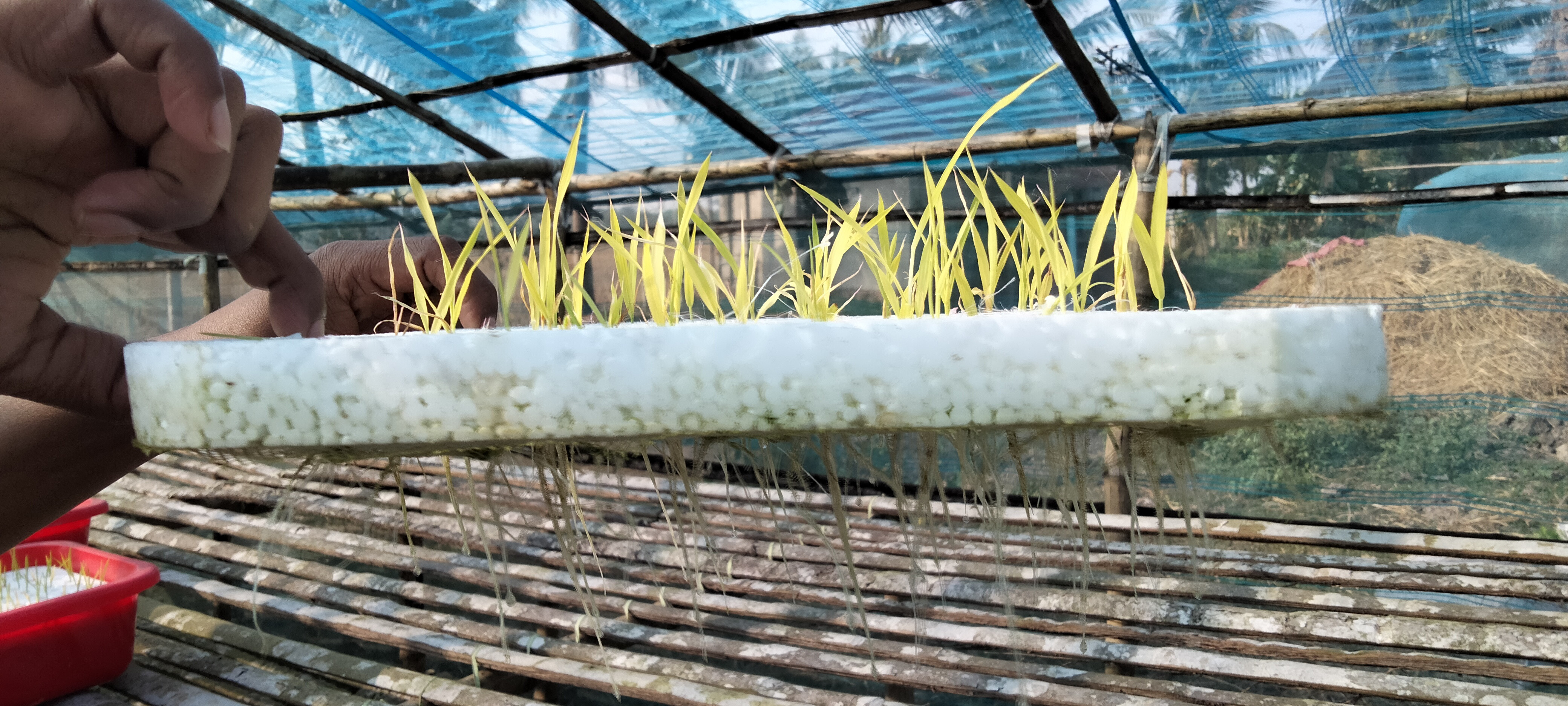
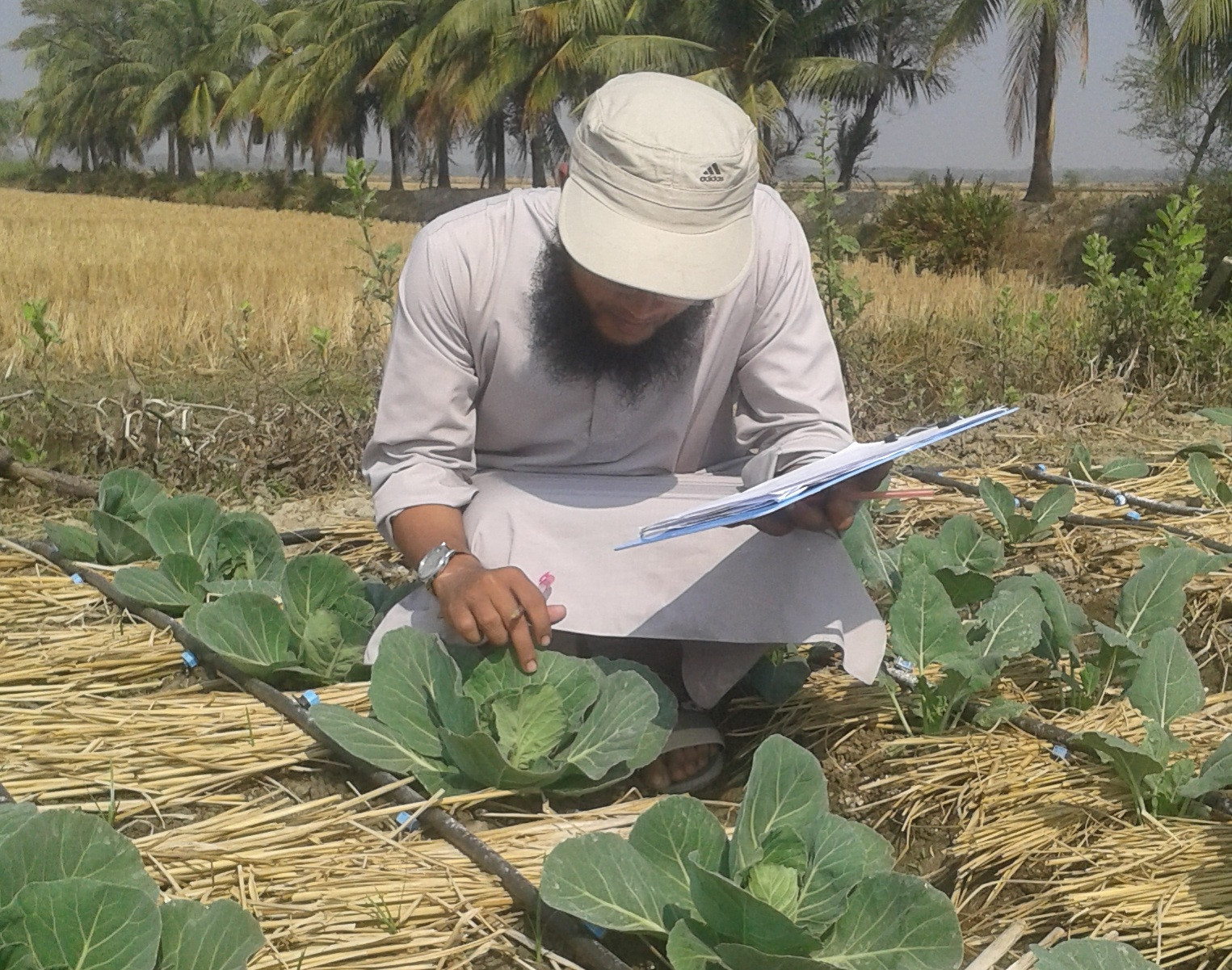




_1732881210.jpeg)